Smart Test Coverage Companion
AI-powered test generation that turns logs into actionable insights
Summary
The Smart Test Coverage Companion leverages large language models and runtime analyzers to automate test case generation, prioritization, and exploratory testing for QA Testers. By transforming requirements, logs, and failing runs into actionable test cases, it helps teams increase coverage, reduce manual effort, and focus on high-risk areas—all while integrating seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines.
Business Problem & Value
QA teams often struggle with incomplete test coverage, flaky tests, and manual prioritization, leading to missed regressions and slower releases. This tool automates test generation, surfaces regression-prone areas, and guides exploratory testing, enabling faster triage, higher coverage, and fewer production escapes—without sacrificing human oversight.
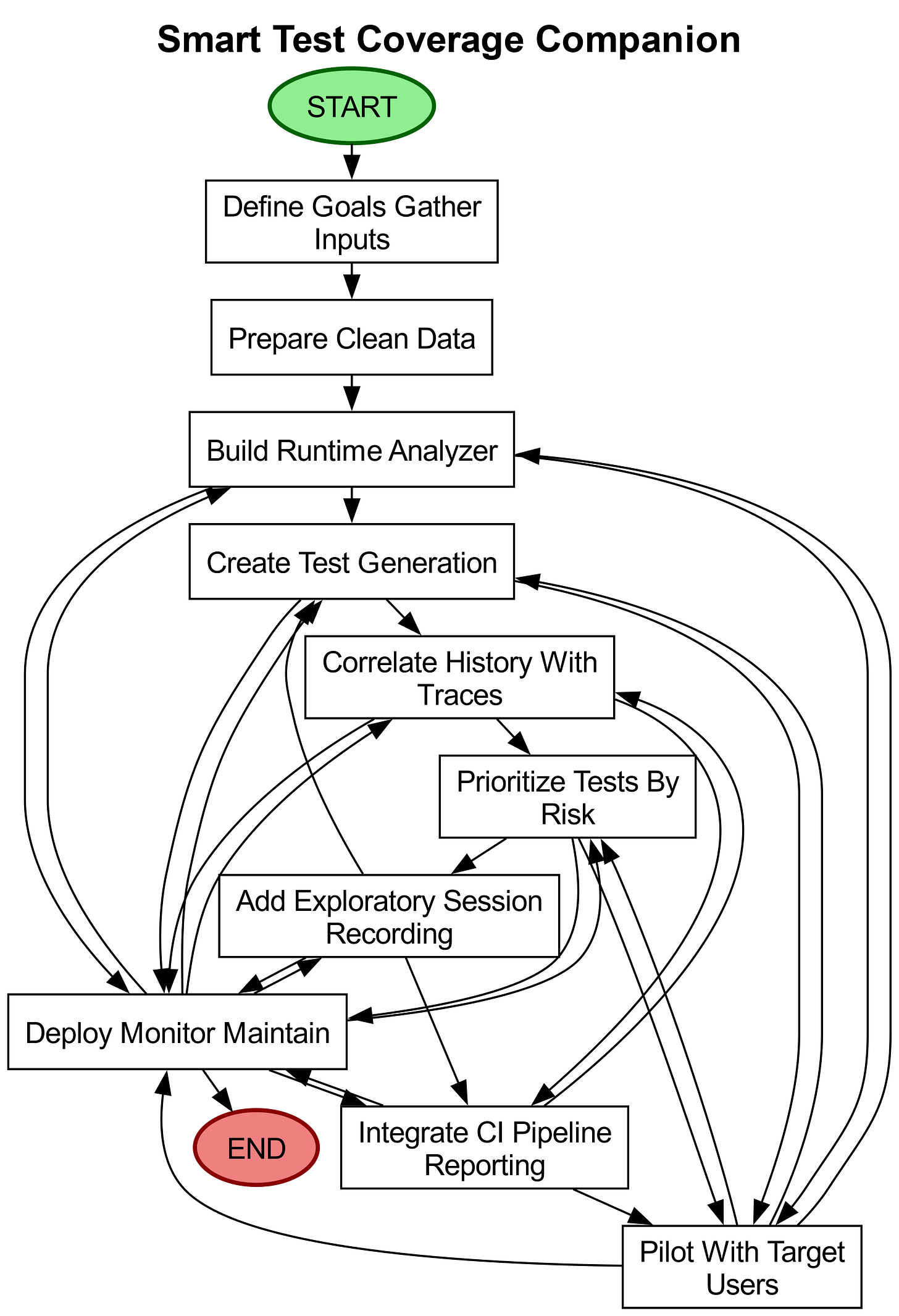
Steps to Build
Define goals and gather inputs: Collaborate with QA leads and developers to outline success metrics (e.g., faster triage, fewer missed regressions). Identify data sources like requirements, test history, logs, and CI pipeline results, while ensuring sensitive data is flagged and access-controlled.
Prepare and clean the data: Collect a representative sample of past test runs, failure reports, and logs. Anonymize or mask sensitive information, then link requirements to tests and code areas using tags or folder structures for traceability.
Build the lightweight runtime analyzer: Implement minimal instrumentation to record code execution during tests, capturing traces or function calls without slowing performance. Store traces with timestamps and identifiers for cross-run comparison.
Create the test-generation module: Use a language model to convert requirements, failure messages, and logs into human-readable test cases and exploratory prompts. Design standardized templates (e.g., input, expected behavior, setup steps) to ensure consistency.
Correlate history with traces to find hotspots: Combine test history (failures over time) with runtime traces (active code during failures) to identify flaky or regression-prone areas. Use simple counts and recency weighting for transparent, tunable logic.
Prioritize tests by risk: Rank tests using signals like recent failures, coverage gaps, code churn, and hotspot counts. Provide a ranked list with clear reasoning so testers understand prioritization decisions.
Add exploratory testing helpers and session recording: Equip testers with guided prompts and a recorder to capture steps, screenshots, and traces during exploratory sessions. Allow notes and issue flagging, storing sessions for future test generation.
Integrate with CI pipelines and reporting: Connect prioritization to CI pipelines to run high-risk tests first and feed results back into the system. Deliver dashboards or daily reports showing coverage trends, flaky tests, and regression hotspots.
Pilot with target users and iterate: Conduct a time-boxed pilot with QA testers and developers. Gather feedback on generated tests, false positives, and gaps, then refine prompts, prioritization rules, and trace collection based on results.
Deploy, monitor, and maintain: Roll out gradually with role-based access controls for logs and recordings. Track accuracy and noise metrics, schedule periodic reviews to update prompts/rules, and enable testers to approve or correct generated tests for continuous improvement.
Impact Metrics
Human-in-the-Loop
Define success metrics and link requirements to tests to ensure traceability and relevance.
Review and approve generated test cases before they are trusted in pipelines to catch errors or gaps.
Triage flagged regressions and flaky areas, investigating root causes and refining prioritization rules.
Run pilots and provide feedback to iteratively improve test generation, prompts, and trace collection.
Set privacy and access controls for logs and recordings to protect sensitive data.
Things to Watch For
Sensitive data exposure: Logs and session recordings may contain private information; anonymization and access controls are critical.
Overconfidence in generated tests: Automated tests may miss edge cases or contain errors, requiring human review to avoid false security.
Noisy signals and misprioritization: Flaky tests or sparse history can lead to incorrect rankings, necessitating ongoing tuning and monitoring.
Key Takeaways
AI augments, not replaces, QA testers by automating repetitive tasks (test generation, prioritization) while keeping humans in the loop for oversight and refinement.
Traceability and transparency are key—linking requirements to tests and providing clear prioritization reasoning builds trust in the system.
Continuous iteration is essential to adapt to changing codebases, reduce noise, and improve accuracy over time.
Disclaimer: The idea discussed here reflects a potential application of AI. It is intended for exploration and inspiration. Actual implementation may vary.